This is an archive of information released in the past.
Disclaimer: It may contain broken links or outdated information. Some parts may not function in current web browsers.
*Visit https://humans-in-space.jaxa.jp/en/ for the latest information.

Mission
Kibo’s Assembly Missions
Kibo’s ISS Assembly Mission Insignias (official JAXA mission patches for each of the Kibo assembly missions)
Kibo is an International Space Station (ISS) module which JAXA operates with the ISS Program. Kibo’s functions are similar to the other ISS experiment modules including the Destiny and Columbus laboratories. However, Kibo has been designed with distinctive characteristics. Kibo is a complex facility that consists of several components and possesses every function that’s required to conduct experiment activities in space. Kibo facilitates experiment activities on orbit. However, Kibo’s utilization is not limited to on-orbit experiments. JAXA plans on expanding the opportunities for extensive utilization of the space environment, including cultural and educational activities.
The six Kibo elements are 1) the Pressurized Module (PM), 2) the Exposed Facility (EF), 3) the Experiment Logistics Module-Pressurized Section (ELM-PS), 4) the Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section (ELM-ES), 5) the Remote Manipulator System (JEMRMS) and 6) the Inter-Orbit Communication System (ICS). The ELM-PS, the PM, the JEMRMS and the pressurized part of the ICS were delivered and installed on the ISS during the STS-123 (1J/A) and STS-124 (1J) Missions in the early 2008. The rests of the components, the EF and the ELM-ES are scheduled to join the ISS in 2009.
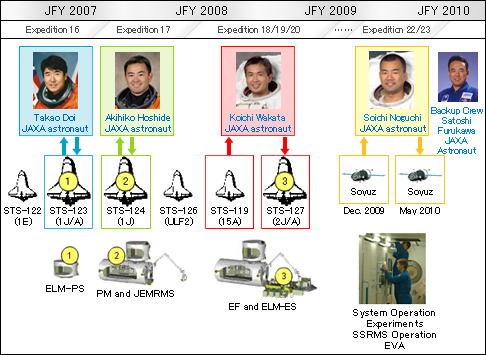
Launch schedules of Kibo’s components and JAXA Astronauts
In mid-March 2008, astronaut Doi flew to the ISS with Kibo’s stowage module, ELM-PS. Astronaut Hoshide flew to the ISS with Kibo’s main experiment module, PM, and Kibo’s robotic arm, JEMRMS in June 2008.
Astronaut Wakata will fly to the ISS during the STS-119 Mission, and he’ll remain on board the ISS as an ISS Expedition 18 Flight Engineer. Astronaut Wakata will await the arrival of Kibo’s external experiment platform and external stowage pallet that will be delivered during the STS-127 (2J/A) Mission.
-
In the ISS assembly mission designators, the “J” represents the missions related to Japanese elements, and the “A” represents the missions related to American (US) elements. For example, 2J/A is the second assembly mission and will deliver Japanese and US elements.
| Copyright 2007 Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency | Site Policy |