This is an archive of information released in the past.
Disclaimer: It may contain broken links or outdated information. Some parts may not function in current web browsers.
*Visit https://humans-in-space.jaxa.jp/en/ for the latest information.

Experiment
- News
- Kibo Utilization Strategy
- Kibo Utilization Plan
- List of JAXA's Utilization Themes
- Experiment Facilities
- Space Environment Utilization
- Archive
News
"Effect of microgravity on osteoclasts and the analysis of the gravity sensing system in medaka (Medaka osteoclast)" experiment has been completed (January 29, 2013)
Medaka osteoclast experiment was performed for about two months, from Friday, October 26, 2012, to Monday, December 24, 8:23 p.m.
Ionosphere, Mesosphere, upper Atmosphere, and Plasmasphere mapping (IMAP) mission obtained its first observation data (January 28, 2013)
Imagers for Ionosphere, Mesosphere, upper Atmosphere, and Plasmasphere mapping (ISS-IMAP) mission installed to the Exposed Facility (EF) of Kibo on the International Space Station (ISS) obtained its first observation data.
"In-situ" observation experiment measuring the precise growth rate of protein crystals on board Kibo has been completed (January 22, 2013)
"In-situ observation of growth mechanisms of protein crystals and their perfection under microgravity (NanoStep)" has been completed.
"Effect of microgravity on osteoclasts and the analysis of the gravity sensing system in medaka" (Medaka osteoclast) has started on board Kibo (November 9, 2012)
A life science experiment "Effect of microgravity on osteoclasts and the analysis of the gravity sensing system in medaka" (Medaka osteoclast), which uses the Aquatic Habitat (AQH) has started on board Kibo, the Japanese Experiment Module.
JAXA's Education Payload Observation (EPO) "How to live comfortable in space" was performed on board Kibo (November 8, 2012)
JAXA's Education Payload Observation (EPO) "How to live comfortable in space - a basic research on the room-size designing of a building in space based on human psychology and movement under microgravity" was performed on board the Japanese Experiment Module, Kibo.
"Mechanisms of Gravity Resistance in Plants" experiment has started on board Kibo (November 5, 2012)
JAXA's life science experiment "Mechanisms of Gravity Resistance in Plants - From Signal Transformation and Transduction to Response" (Resist Tubule experiment) has started.
Successful extension of the Inflatable Material experimental Panel (IMP) in the series of the SIMPLE (November 1, 2012)
At 9:10 p.m. on August 24, 2012, the shape-memory polymers in the exposed environment were extended successfully, as one of the series of the Space Inflatable Membranes Pioneering Long-term Experiments (SIMPLE).
Operational checkout was performed for the Robot Experiment on JEM (REX-J), as one of the MCE missions (October 31, 2012)
JAXA has confirmed that the robot's basic function is properly working during the checkout performed from August 20 to 31, 2012, for the Robot Experiment on JEM (REX-J), one of the Multi-mission Consolidated Equipment (MCE) mission experiments.
COTS HDTV-EF successfully obtained Earth surface video image under the space environment (October 30, 2012)
On August 19, 2012, JAXA's COTS HDTV -EF video camera installed on the MCE of the Exposed Facility of Kibo, has successfully obtained the high definition video image of Earth for the first time in the world as a commercial-off-the-shelf product sold to the public.
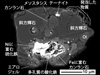
The world's first discovered extraterrestrial material captured from the ISS (October 26, 2012)
The Micro-Particles Capturer and Space-Environment Exposure Device (MPAC&SEED); payloads developed by JAXA, which were installed on the exposed portion of Zvezda of the ISS, has been found to have captured a new extraterrestrial material with unprecedented mineralogical characteristics
| Copyright 2007 Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency | Site Policy |