JAXA Astronaut Activity Report, January 2008
Last Updated: March 21, 2008
This is JAXA's Japanese astronaut primary activity report for January 2008.
ISS Emergency Procedure Training

Astronaut Hoshide (center), his STS-124(1J)Mission crewmates, and ISS Expedition 17 crew members participating in the training
Astronaut Akihiko Hoshide, his STS-124(1J) crewmates, and the ISS Expedition 17 crew members that are assigned to be aboard the ISS when the STS-124 mission crew arrives, participated in ISS emergency procedure training using the ISS full-scale mock-up training facility at the NASA Johnson Space Center (JSC).
The training was conducted under the assumption that a fire had broken out in Harmony (Node 2) while preparing for an Extravehicular Activity (EVA). Following fire emergency procedures, the ISS Expedition 17 crew members located and suppressed the fire, while the STS-124 mission crew members swiftly evacuated to the space shuttle and closed the hatches between the ISS and the space shuttle.
- STS-124(1J) Mission
NASA-JAXA Joint Multi-Segment Training
Astronaut Takao Doi and his fellow STS-123 (1J/A Flight) Mission crew members participated in the Joint Multi-Segment Training (JMST) that simulated mission-specific operations and communication procedures that are planned for the STS-123 Mission.
During the JMST, which lasted 39 hours, the astronauts simulated a series of operational procedures scheduled for Flight Days 3 and 4, including the space shuttle docking to the ISS, the first EVA, and the attachment of Kibo‘s Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section (ELM-PS) to the ISS.
During the training, Astronaut Doi simulated the operation of the space shuttle’s robotic arm, the Shuttle Remote Manipulator System (SRMS), and simulated attaching the ELM-PS, while coordinating these operations with the JAXA and NASA flight controllers that are assigned to support the STS-123 Mission.
- STS-123(1J/A)Mission
- Experiment Logistics Module (Pressurized Section)
Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) on Kibo’s Pressurized Module

STS-124 crew members examining the MLI covers that protect the joint of Kibo's robotic arm, the JEM Remote Manipulator System (JEMRMS)
At the NASA Kennedy Space Center (KSC), astronaut Hoshide and his STS-124 (1J) Mission crewmates conducted a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) on Kibo’s Pressurized Module (PM).

STS-124 crew members examining the Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) of Kibo’s Pressurized Module (PM)
During the CEIT, the assigned crew members have the opportunity to verify the flight readiness of the equipment that they will actually be using during their mission.
Astronaut Hoshide and his STS-124 crewmates checked the locations of the valves inside the PM, and reviewed their planned intra-vehicular activities and procedures, including removing transfer bags attached to the front of Kibo’s system rack, and removing the cover from the Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) that covers the CBM from the inside of the PM. The astronauts also examined the equipment labels on board the PM. In addition, the astronauts reviewed the procedures for disconnecting the PM Launch to Activation (LTA) heater cables that will supply power from the space shuttle to the PM heaters during launch, and removing the Multi Layer Insulation (MLI) covers from the joints of the Kibo’s robotic arm, the JEM Remote Manipulator System (JEMRMS) and the CBM outside of the PM. These tasks will be carried out during one of the STS-123 Mission’s EVAs.
- STS-124(1J) Mission
- Pressurized Module (PM)
- Remote Manipulator System
Training for exercise equipment
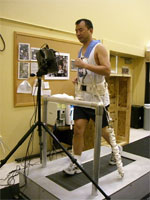
Astronaut Noguchi using a treadmill

Astronaut Wakata using an ergometer-equipped exercise bicycle
At the NASA Johnson Space Center (JSC), astronauts Wakata and Noguchi participated in training on how to use the exercise equipment on board the ISS.
The astronauts learned how to use the treadmill, the ergometer-equipped exercise bicycle, and a resistive exercise device that are currently used on board the ISS, and a new treadmill that will be delivered to the ISS in the future.
This new treadmill is designed with a structure that dampens the vibration transmitted to the ISS, and includes a function that records a log of the crew members’ exercise.






