Cargo in the pressurized Logistic Carrier (PLC)
Utilization/experiment related items
- Cell Biology Experiment Facility-Left (CBEF-L)
-
The Cell Biology Experiment Facility-Left (CBEF-L) will be used along with the Cell Biology Experiment Facility (CBEF), which is currently being utilized on the KIBO, in order to expand its use for life science experiments.
As improvements to the CBEF, the CBEF-L as equipment for experiments can now decrease the gravity difference due to the artificial gravity generator with more than doubled radius as well as breed animals larger than mice.
- Small Optical Link for International Space Station (SOLISS)
-
Small Optical Link for International Space Station (SOLISS) is a small-sized satellite optical communication system collaboratively developed by Sony Computer Science Laboratories, Inc. and JAXA Space Exploration Innovation Hub Center in order to conduct in-orbit technology demonstrations. The SOLISS was developed based on the infrastructure technology collaboratively researched by Sony Corporation and JAXA Space Exploration Innovation Hub Center.
For the in-orbit demonstrations, the SOLISS is installed on the IVA-replaceable Small Exposed Experiment Platform (i-SEEP), which is installed on the out-board platform for experiments of the KIBO on the ISS. The communication demonstrations with the ground are conducted by using the 1550nm laser.
- Gravitational Dependence Research of Flexible Surface on a Planet (Hourglass)
-
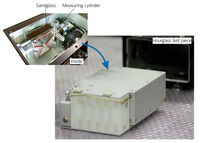
Hourglass is an experiment that utilizes the CBEF (artificial gravity generator) only possessed by the Japanese Experiment Module, KIBO. The objective is to research the effects that micro and low gravity has on the characteristics of powder and granular materials. The research is conducted by loading hourglass-type and measuring cylinder-type equipment with powder and granular materials such as simulated sand of a planet and/or the moon in them on the CBEF.
- JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD) and Ultra-small Satellite (CubeSat)
-
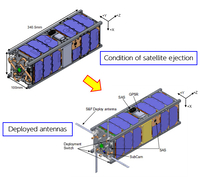
An ultra-small satellite collaboratively developed by Kyushu Institute of Technology and National Authority for Remote Sensing and Space Science (NARSS) as well as other ultra-small satellites developed by Space BD Inc. and The University of Tokyo will be transported and deployed from the KIBO.
Reference:
- Ultra-small Satellite (CubeSat)
- NARSSCube-1 (Kyushu Institute of Technology/National Authority for Remote Sensing and Space Science (NARSS))
Development, operation of a satellite, and a demonstration experiment with a 200m resolution camera installed on the satellite by our research partner, Egypt. - AQT-D (Space BD Inc./The University of Tokyo)
Technology demonstration of a resistojet thruster module that uses 1U size of water as propellant and communications with the mountainous terrain using a UHF antenna. - RWASAT-1 (The University of Tokyo/Ministry of Commerce, Industry, & Tourism Rwanda Utilities Regulatory Authority Smart Africa secretariat (Republic of Rwanda))
For human resources development of researchers in Republic of Rwanda and technological improvement. A radio wave (weak) receiver is installed and collects sensor information on the ground.
- NARSSCube-1 (Kyushu Institute of Technology/National Authority for Remote Sensing and Space Science (NARSS))
- Ultra-small Satellite (CubeSat)
- Fresh food
-
HTV8 will also deliver fresh food.
- ISS battery Orbital Replacement Units (ORUs)
-
Following HTV6 and HTV7, HTV8 delivers new lithium ion batteries for the ISS. The batteries are delivered on the Exposed Pallet (EP), placed on the Unpressurized Logistic Carrier (ULC).
The new six battery Orbital Replacement Units (ORUs) consist new lithium-ion battery cells manufactured by a Japanese company.
The nickel-hydrogen batteries currently used on the ISS are becoming old. The extension of ISS operations becomes possible with the supply of Japanese lithium-ion battery cells. Only the HTV is capable of delivering six battery ORUs at one time, and thus plays an important role in continuous ISS operations.
Cargo for the ISS crew
Cargo on the Unpressurized Logistics Carrier (ULC)
*All times are Japan Standard Time (JST. UTC + 9 hours)