| STS-95 Payloads |
 |
 |
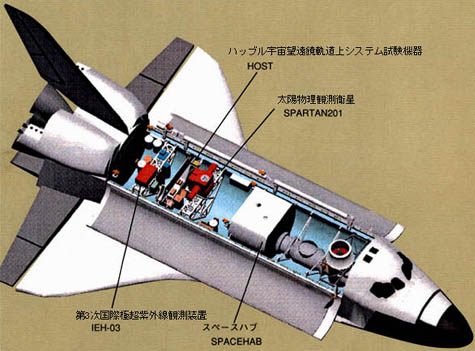
Four primary payloads of STS-95 are |
|
| 1. |
SPACEHAB
SPACEHAB is a space laboratory pressurized to about one atmosphere, flown
in the payload bay of the Shuttle. SPACEHAB is developed and operated by
an American private company, SPACEHAB, Inc. SPACEHAB has been flown board
the Shuttle since 1993, and the current mission will mark the twelfth SPACEHAB
flight.
There are two types of SPACEHAB: the single-module type and double module
type (about twice the volume of the single module), applied in accordance
with the objective of each mission. STS-95 will use the single module.
Experimental units are installed in racks and lockers inside SPACEHAB.
Power supply, cooling, exhaust gas vent, and communication capability is
provided through these racks and lockers.
|
 |
|
SPACEHAB interior
The small boxes attached to the wall are lockers.
The racks are at the far side.
|
|
Illustration supplied by SPACEHAB,Inc.
|
|
| 2. |
Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test
Platform (HOST)
The HOST was developed to test and verify the new components and technology
to be used during the Hubble Space Telescope servicing mission scheduled
for May 2000.
The HOST carries the following.
- NICMOS Cooling System
A new cryostat substitute for solid nitrogen, which is currently used as
the coolant for the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer
(NICMOS), verifies to enable long-duration operation.
- HST 486 computer
As a substitute for the currently used DF-224 computer processor (CPU),
a new 486 CPU is confirmed to have a superior resistance to space radiation.
- Optical fiber
The transmission performance of optical fiber under high radiation environment
is confirmed.
- Solidstate data recorder
The currently used tape recorder undergoes comparative function testing
to assess resistance to space radiation.
|

|
| Hubble Space Telescope (HST) |
|
3.
|
SPARTAN 201
The main objective of the SPARTAN 201(Shuttle Pointed Autonomous Research
Tool for Astronomy) mission is to verify the mechanism of acceleration
of solar wind generated from the corona of the Sun and the mechanism of
heating of the corona.
SPARTAN 201 is a reusable, free-flying satellite for solar physics observation
released from and retrieved by the Space Shuttle. During the STS-87 mission,
NASDA Astronaut Takao Doi and his crewmate manually captured this satellite.
This is the fifth flight for SPARTAN since its space debut in 1993.
|
 |
| SPARTAN201 |
|
| 4. |
IEH is a mission to observe the Sun, Jupiter,
and celestial bodies outside the solar system by extreme ultraviolet rays.
Following flights in September 1995 and August 1997, this is the third
IEH flight.
The IEH-03 carries the following experimental units.
- Solar Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker
To study the upper layer of the Earth's atmosphere, this unit measures
emissions of extreme ultraviolet rays and super ultraviolet rays beamed
from the Sun to the Earth.
- Ultraviolet Spectrograph Telescope for Astronomical Reserch
Ultraviolet Spectrograph Telescope for Astronomical Reserch (UVSTAR) unit
acquires extreme ultraviolet spectra images sent from the plasma torus
of the Jupiter satellite IO, and from the plasma sources of ultra-high-temperature
stars.
- STAR-LITE
This unit observes supernovas remnants, star forming regions in external
galaxies, and etc.
- Solar Constant Experiment
Solar Constant Experiment (SOLCON) unit accurately measures variations
in the value during a solar cycle and the Solar Constant.
Several other secondary experimental units are also installed in the IEH-03.
- Petite Amateur Navy Satellite
Petite Amateur Navy Satellite (PANSAT) is released from the Space Shuttle
into an orbit, the PANSAT satellite engages in digital communications between
ground stations. PANSAT is a spacecraft polyhedral in shape and 48 cm in
diameter. The satellite will not be retrieved.
- CONCAP-IV
Utilizing the vapor migration in the zero-gravity environment, an experiment
is conducted on the growth of Non-Linear optical (NLO) organic materials.
- GAS-764
This unit conducts an experiment simulating dust aggregation the dynamics
of dust clouds and the gathering of dust in the early solar system using
small glass particles in a vacuum chamber.
- GAS-238
|
|
 |
Layout of payloads on STS-95 |
| Last Updated: November 10,1999 |

|
