<Outline of Experiment>
Astronauts showed muscle atrophy after space flight, even though they made
efforts to do exercise during the flight. Skeletal muscle is composed of
two types of muscle fibers; 1) fast muscle fibers which bear fast and large
contraction within short period of time 2) slow muscle fibers which carry
slow but continuous contractions for a longer period. The main structural
proteins of skeletal muscle are myosin heavy chains (MHC), which have fast
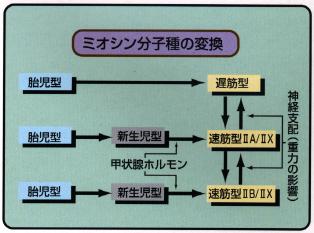
and slow isoforms. Under the influence of microgravity, slow muscle fibers
tend to show atrophy and are turned to be fast muscle fibers, but the molecular
mechanism of this phenomenon is unclear and remains to be solved.
In the Neurolab experiments, we would examine the expression of muscle
specific proteins along the development of neonatal skeletal muscle under
the microgravity. Especially, the influence of gravity on the transition
of MHC isoforms would be analyzed in detail at protein level and mRNA level.
<Expected Outcome>
This study would provide new aspects of molecular background of muscular
atrophy due to microgravity and might give new idea on preventing muscular
atrophy during space flight.
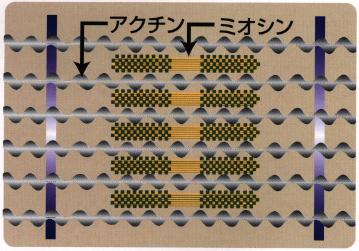 |
Structure of muscle fibers |
|
 |
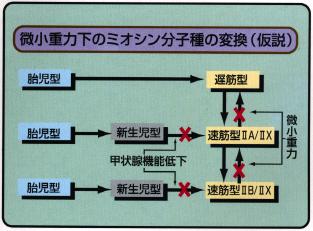 |
| Flow-chart of fast muscle fibers and Slow muscle fibers |
|
Last Updated : March 27, 1998


