<Background and Objectives>
The blood circulation in the human and mammals is regulated by various
mechanisms. Baroreflex is one of these mechanisms and contributes to stabilization
of blood pressure in the following manner. When blood pressure increases,
the sensors called baroreceptors which are free ends of autonomic nerve
fibers distributed in the wall of some arteries are excited with a stretch
of the arterial wall due to the increase of blood pressure. The excitation
travels to the special nerve calls located in the brainstem where the signal
is transferred to other cells and modified, and finally motility of the
heart and vessels is changed by signals from the brain via the sympathetic
or parasympathetic nerve of the autonomic nervous system, the origin of
which is located in the spinal cord or brain stem. Then blood pressure
returns to the original level.
The aortic nerve is one of the afferent pathways of the baroreflex, and
distributes in the walls of the aortic arch and the right subclavian artery.
The principal investigator, Shimizu previously found that the aortic nerve
develops structurally and functionally during growth. To investigate the
effect of microgravity on the development of the baroreflex system, they
send young rats with their mother rat to space and raise them for 17 days,
and after landing they test the baroreflex ability by electrophysiological
methods as well as examine various tissues including the aortic nerve,
heart and vessels with an electronmicroscope.
<Results and Earth-based Benefits>
It is expected from the experiment to obtain important informations about
the mechanism of cardiovascular deconditioning during inflight or postflight
and basic knowledges for countermeasures to the deconditioning as well
as about adaptation to the space environment in the cardiovascular regulation
system.
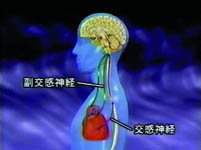 |
 |
Sympathetic nerve and parasympathetic
nerve to control the reflection of
blood pressure |
Cross section of the Rat Aortic nerve |
|
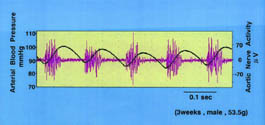 |
 |
Blood pressure curve and Aortic Nerve
Activity in the Rat |
Young Rat |
|
Last Updated : March 27, 1998


