| EVA |
 |
 |
|
|
|
What's EVA? |
- EVA stands for ExtraVehicular Activity. Commonly referred to as a space
walk, astronauts will perform tasks outside the spaceship, in space or
on the surface of the moon or on other celestial bodies.
The first spacewalk in human history was performed by astronaut Leonov
of the former USSR out of Voskhod-2 on March 18, 1965. His spacewalk lasted
24 minutes.
Astronaut Edward White aboard Gemini No.4 was the first American astronaut
to venture an EVA on June 3, 1965.
In the US space project,EVAs were continued throughout the Apollo mission
to the Skylab, then to the Space Shuttle program. Throughout these experiences,
remarkable improvements were made in the EVA unit and EVA support systems.
To prepare for the International Space Station (ISS) era. ISS assembly
procedures, operability and performance tests of required tools, and procedures
to train astronauts for EVA were tested and validated during recent EVA
missions. Improved EVA technologies have made it possible to capture and
repair satellites. A typical example was the mission to capture the Intelsat-6
satellite to replace its rocket motor. Another significant event was the
capture the Hubble Space Telescope to improve its performance.
Astronauts conducting EVA needs protection from the space environment.
The system developed is called an EMU consisting of the life support system
(LSS) and a spacesuit.
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
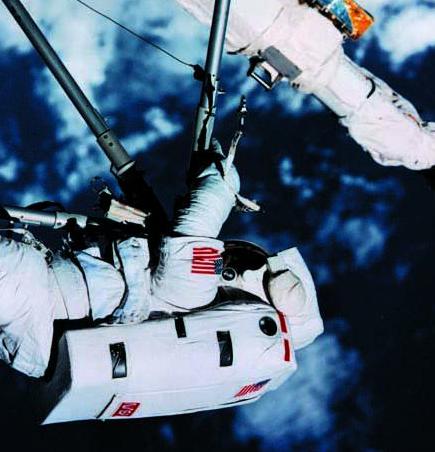
| EVA on STS-49 |
|
|
|
|
Astronaut Scott performing
EVA on STS-72
|
- The astronauts' EVA will be conducted in accordance will the following
procedures:
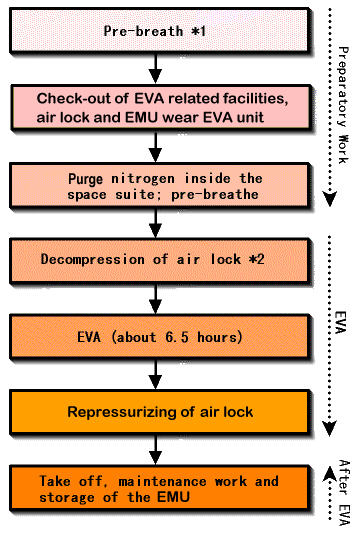
*1 Pre-breathe
- Put on his helmet and inhale pure oxygen for about 60 minutes. Then
the pressure inside the Shuttle will be depressed from 14.7 psi to 10.2
psi for more than 12 hours.
- The nitrogen inside the space suit will be discharged, and the astronaut
will inhale pure oxygen for 40 to 75 minutes. Then the space suit pressure
will be decompressed to about 4.3 psi, and the EVA will begin.
*2 Air Lock
-
This is an airtight chamber permitting passage to or from
the shuttle to outer space. It allows an astronaut wearing the EMU to
go out or to return to the spacecraft without decompressing the Spacecraft
cabin.
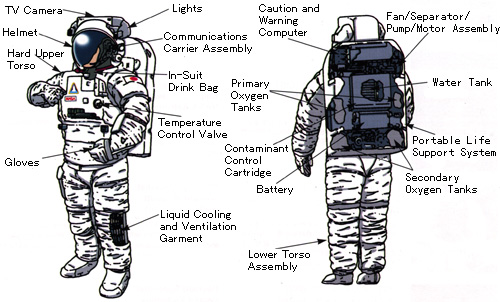
- The EMU consists of the Life Support System (LSS), the Space Suit Assembly
(SSA), and Support Equipments. The EMU is indispensable to sustain life
and to enable astronauts to work in space.
|
|
: |
Controls pressure and temperature inside the SSA. Supplies
oxygen and power.
|
|
|
: |
Covers the upper and lower parts of the body including
gloves and helmet. A liquid cooling and ventilation garment and a headset
for communications in worn underneath.
|
|
|
: |
In-suit drink bag, EVA Helmet light, TV camera. |
Last Updated : November 4, 1997





