
| Electromagnetic Compatibility Test of Kibo's manipulator
main arm |
|
An Electromagnetic Compatibility Test
of Kibo's manipulator main arm was conducted at the Tsukuba Space Center from
Oct 5 to Oct 19, 1999.
 | What
is an Electromagnetic Compatibility Test? |
| |
| Electromagnetic Compatibility
Test Facility | Kibo's onboard equipment must be
able to operate as designed, but that is not enough. NASA also needs to confirm
that the noise this equipment generates does not affect other equipment inside
Kibo or the International Space Station (ISS). Similarly, NASA must also confirm
that the equipment is not affected by the noise generated by other equipment.
Two types of Electromagnetic Compatibility tests were conducted to confirm
the conditions above. A noise radiation test was conducted, in which the frequency
and the level of the noise that Kibo's main arm generates were measured to confirm
that the main arm does not affect other electric and electronic devices. A radio
sensitivity test was also conducted to confirm that the manipulator main arm functions
appropriately without being affected by the noise generated by other electric
and electronic devices.
This Electromagnetic Compatibility Test is being
conducted on electric and electronic devices such as PCs, printers and microwave
ovens. Every country has Electromagnetic Compatibility regulations. Products that
do not satisfy these regulations are not allowed to be distributed in that country's
market.
Several methods are being devised to suppress radio frequency
noise, such as grounding, twisted-pair cable, and shielded cable the core of which
is covered by a shield which is made of netted thin conductive lines.
 | What
is Kibo's Manipulator? | 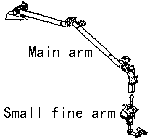 |
| Main arm
and small fine arm | Kibo's
manipulator is a robot arm composed of three elements; the main arm, which
is used to manipulate heavy objects up to maximum seven tons; the small fine arm,
which is attached to the end of the main arm to be used to perform fine manipulation
for up to maximum 300kg objects, and the manipulator console to control both arms.
This manipulator supports experiments and maintenance operations by exchanging
equipment on Kibo's Exposed Facility.
 | What
measurements are conducted in the Electromagnetic Compatibility test. |
 |  | Noise
radiation test |  |
 |
| Noise wave measurement |
This test measures the level of noise generated by the main arm. For this
test, the main arm was placed in a shield room and the joint motors were drove
by supplying power and control signals. A shield room is
a room which is protected against external radio wave and is free from internal
radio wave reflection. The frequency of the noise generated by the main arm ranges
from 14KHz to 15.5GHz. By changing the receiving antenna according to the target
frequency bands, the noise level were recorded. As a result, the main arm noise
level was confirmed to be lower than the threshold indicated below.
Noise radiation test threshold
| Frequency |
Main arm noise radiation level | | 14KHz
to 10MHz | Within 56dB microV/m |
| 10MHz to 259MHz | For different
frequencies, within 56 to 86 microV/m |
| 259MHz to 10GHz | For different
frequencies, within 46 to 72dB microV/m |
| 13.5GHz to 15.5GHz | Within 76dB
microV/m |
Driving the main arm is an ideal method for measuring the noise level. However
since the main arm is designed to be driven in a microgravity environment, only
the motor was driven so that excessive load will not be imposed on the main arm's
components.
|  | Radio
wave sensitivity test |  |
 |
| Noise radiation |
This test is conducted to confirm that the main arm is not affected by
external noise. Again, the main arm was placed in the shield room and a wide frequency
range of noise between 14KHz to 15.5GHz was applied to the main arm following
the rule shown below. This is the reverse of the noise radiation test. Under this
condition, a control signal was sent to the main arm to drive it, and the reaction
signal from the main arm was recorded. The main arm was confirmed to be free from
the noise generated by other equipment by confirming that the recorded signal
is normal.
Radio sensitivity test threshold
|
Frequency | Noise
radiation level surrounding the main arm | | 14KHz
to 200MHz | 5V/m | | 200MHz
to 8GHz | 60V/m |
| 8GHz to 10GHz | 20V/m |
| 2.2GHz | 161V/m |
| 8.5GHz | 79V/m |
| 14.8GHz to 15.2GHz | 250V/m |
|
 | Shield
room |  |
| Shielded room |
The shield room is protected from externally generated radio signals.
In addition, all room walls are covered with material that absorbs radio signals,
so that radio signals are not reflected inside the room. We are surrounded by
broadcast and communications radio signals. A shield room enables us to measure
radio signal levels without influence of other radio signals.
 | Future
tests planned for the main arm | In the future, two tests
are scheduled to be conducted on the main arm. A Modal Survey test will be conducted
to confirm the vibration frequency that causes resonance in the main arm. A functional
test will be conducted by driving the main arm on the horizontal plane to confirm
that the main arm functions normally. These two tests will conclude the series
of tests conducted only on the main arm itself. Following these tests, an integrated
system test will be conducted, with the manipulator connected to the manipulator
console.
Last Updated : December 20, 1999
|

