This is an archive of information released in the past.
Disclaimer: It may contain broken links or outdated information. Some parts may not function in current web browsers.
*Visit https://humans-in-space.jaxa.jp/en/ for the latest information.

Experiment
- News
- Kibo Utilization Strategy
- Kibo Utilization Plan
- List of JAXA's Utilization Themes
- Experiment Facilities
- Space Environment Utilization
- Archive
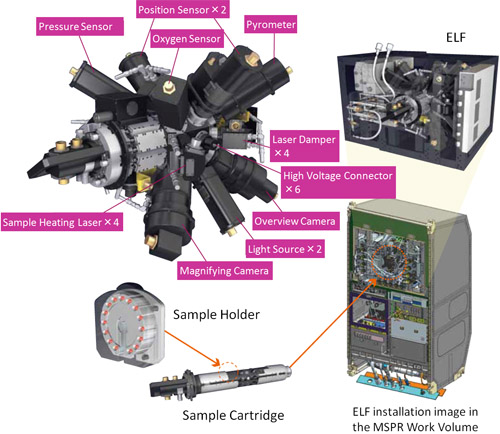
Electrostatic Levitation Furnace (ELF)
Levitation of a sample in the ELF
 |
 |
 |
 |
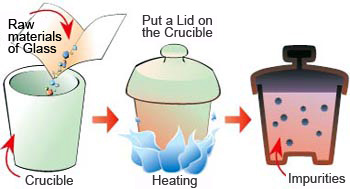
Making Materials Free of Impurities
How to Make Glass on Earth
You probably have watched the image of astronauts playing with a round water drop floating in the air on TV. A levitation furnace is an instrument that is similar in concept to that of the floating water drop. The electrostatic levitation furnace (ELF) is a payload for material science in which a variety of materials can be processed without crucibles, by taking advantage of the zero-gravity environment in the Japanese Experiment Module (Kibo) of the International Space Station (ISS).
Why do materials have to be levitated during the experiments ? When we make glass on Earth, a mixture of raw materials are put into a container called a crucible, and the whole crucible is heated to melt the materials. Then the melted materials are cooled down for solidification. In the process of melting raw materials at high temperature, a chemical reaction between the liquid sample and the crucible occurs, which means that impurities from the container are introduced into the raw materials.
To avoid contamination from the crucible, we simply have to stop using the crucible. That is, raw materials should be heated while being levitated. This is a unique processing method which is easily accomplished under the zero-gravity environment.
Levitation of High Temperature Metals by Electrostatic Force
You might think that it is easy to levitate and heat materials in space because there is no gravity. However, various problems occur in space during actual experiments.
If a sample were under zero-gravity without any forces to move it, the sample would remain in the same position. However, it is actually affected by residual gravity, even in space; the astronauts’ movements, the docking of a space shuttle, and the ISS can generate forces which are applied to the sample in various directions. If the sample position is not controlled properly, the material will be moved by these forces, and the experiments will inevitably result in failure. Various technologies have been developed to successfully control the sample position and conduct experiments.
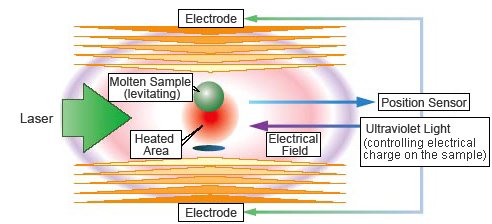
Principle of Electrostatic Levitation
Levitation of objects by electrostatic force
As its name suggests, the Electrostatic Levitation Furnace (ELF) can levitate objects by electrostatic force. In this method, Coulomb forces between a charged sample and surrounding electrodes are actively controlled to maintain the sample position. With this method, various materials, including ceramics, glass, metal, and even water, can be levitated: a floating fish tank can be made, for example.
High-Speed Feedback Control of Materials in the Air
Just levitating a material in the air would let it fly away. Therefore, the ELF controls the material by detecting its position using a position sensor, and giving high-speed feedback of the position signal to the upper and lower electrodes. That means when the material moves to the right, a detected position signal is quickly sent to the electrodes so that they can control the electrostatic force to move the material back to the left.
This method also makes it possible to move the material and fix it at a desired position. It is also possible to rotate the material by shifting the laser from the center.
Melting Materials by Laser
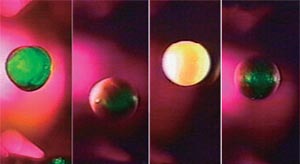
Melting and Solidifying of Ceramics
The levitated material can be heated by irradiating it with separately-controllable lasers. The processes of melting and recrystallization of the material can be observed by using a radiation thermometer and CCD cameras, which are installed around the material.
Specification
| Item | Specification | |
|---|---|---|
Size |
Main body 590(H)x887(W)x787(D)mm UV Lamp 226(H)×259(W)x347(D)mm |
|
Mass in orbit |
Approx. 220kg | |
Maximum power consumption |
Approx. 550W | |
Sample size |
Sample in spheroidal form with φ1.5-2.1 mm (Up to φ5 mm is possible by replacing the cartridge.) | |
Sample |
Mainly oxides Semiconductor, alloy, and metal are also available |
|
Accuracy of positioning |
3 axis control Control period: Max. 1kHz Absolute positioning accuracy: ±100µm |
|
Ambient |
Air pressure: 2 atm (oxygen concentration: 10%), N2: 2 atm, Ar pressure: 2 atm, vacuum (through JEM evacuation line) | |
Heater |
Heating laser (Semiconductor laser, wavelength: 980 mm, maximum optical output: 40 W x 4) | |
Temperature measurements |
Measuring range: 300-3,000°C Sampling rate: 100 Hz | |
Surface tension, viscosity |
Measures surface tension by the resonant frequency of melts, and density by the attenuation rate of vibration. Vibrational excitation (1-600 Hz) | |
Solidification observation |
Resolution: 640 x 480, frame rate: 30 fps, dynamic range: 120 dB or more | |
Magnified measurements |
Using ultraviolet background light for observation at 140 pixels/radius or higher with a diameter of 2 mm,measures the sample's contours of light emitted at high temperatures. | |
- ELF Brochure [PDF 4.30MB]
| Copyright 2007 Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency | Site Policy |